It can be daunting to know the first place to start after you know you want to build a mobile app. We are here to help. We can help you focus in your project goals on what makes sense.
Ultimately only you will be able to provide the core vision for what you need. As you ask the questions below, think through the lens of what needs to be in front of users first.
Let’s Build a Minimum Viable Product
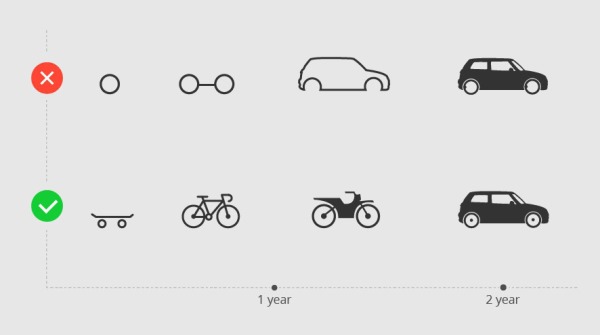
Source: Kunal Naik
Since building technology costs money, having priorities will save you money. So what are the priorities? As we explore this question, keep in mind that it’s always smart to build a minimum viable product (MVP) first. Rather than having a little of everything that works ok, focus on building one aspect of your vision well so that it’s a great foundation. That may mean focusing on one platform before doing both iOS and Android. It may mean we should focus on core functionality before adding extra features.
Have an idea of what’s a must-have versus things that aren’t crucial. This will help you know what you should invest in first. It’s always better to get a smaller, great product in front of users, rather than an app that has more, but doesn’t work great. Having an MVP also helps you get to market faster, which has huge advantages. If you keep launching major updates to your app every 6 months, you’ll be learning what works and what doesn’t. This saves you money since you know which ways you need to pivot your thinking. It often doesn’t make sense to work on a large app for years, without getting feedback from users along the way.
That’s the critical piece of advice I’d give any of my friends who are involved in getting an app built. Keep in mind you’re building a MVP, and not the kitchen sink when considering the questions below. Here are some common questions we get when people reach out for a quote. This should help prepare you for a conversation with us.
Let’s Play Common Questions Bingo
If we wanted to build a Bingo board with the common questions that come up during a conversation about building an app, we’d be winning lots of Bingo. If you don’t know how to answer the questions below, spend some time thinking it over and reach out if you’re stuck. We can point you in the right direction.
You want to know: “How much will it cost?”
We need to know the answer to some of the questions below before we’re able to answer this one for you. In general apps are expensive to build, and zeros are involved. Thankfully a round number can get more focused as we learn more.
So what will we ask to get to the answer for that question?

What’s the big idea?
What makes this app unique and different? What will compel people to use it? What is that one thing that absolutely needs to come across when someone uses this thing?
What kind of features are you envisioning?
What are the core thing someone can do with your app? It can be helpful to see if you can distill your app in 2-3 user stories. A user story is a high-level description of one of the things a user can do with your app. Here are few examples:
- As a car driver I can swipe my app while paying for gas to earn rewards.
- At the gas station, I can show my app to redeem rewards at the counter and get a free Coke.
- As a beer enthusiast I can scan a beer’s barcode to see details about a beer.
- As a movie buff, I can search for a movie and mark it as watched.
Does this need to be an app?
Hang with me. Sometimes people will have an app idea that may not lend itself to the app format. If you want to build an app for writers that helps them build up their typing speed, it may work better as a website or desktop app, where people are more likely to have a keyboard when using it. What’s the advantage to people having this product on the go?
Who is this app for?
What’s your target demographic? Who will be using this app? This can help decide how the user interface works.
How do you plan to make money with this app?
This may sound a big harsh, but what’s the business plan? If you haven’t considered the longterm plan for how the app makes you money or meets your goal, you may be missing a core feature that needs to be in the app.
What’s the play? Should users be able to subscribe monthly to the app? Are there in-app purchases? Are there ads or messages from you or partners? How does a user give you valuable information such as their email address so you can reach out and tell them about your next rally for saving the rainforest? Does your app help you reach your goals?
Do you have a specific timeline in mind?
Do you have time pressures tied to your app? For instance, are you building an app that helps you create custom emojis that you’d like to release on the same week that the next Emoji Movie releases? Or do you have investors or stakeholders with expectations on when the app will be rolled out?
Based on the timeline, we may recommend what would be doable within your desired time window.
What other apps are your competition?
This question helps in a couple ways. Are you building an app that already exists? If so, what is your competitive advantage? If you’re building something different or better than someone else, how will that inform the features you’re wanting?
If you do have competition, what do they do that you also want to do? One advantage to not being the first on the scene, is that you don’t have to re-invent the wheel. You can likely glean from others what is already working in your space.
How fleshed out is the design?
Do you need a designer? Or is everything already mocked up? If you need some help with the ideation phase, we can help figure out a plan. Knowing how far along you are in this step will inform how long the process may take.
What devices will be able to run your app?
On what devices will your app be able to run? Can it only run on iPhones? Or just on Android phones? Both? What about tablets? Should the app look different for users using larger screen sizes? The answers to these questions greatly impact what needs to be built.
What other technology will accompany the app?
- Do you also need a website?
- Does an API need be built so that the app can access the data it needs?
- Do you need an interface that allows you to edit or see user details?
- Do you need analytics about the app so you can see reports of how people are using it?
Bingo!
If you have the answer to 5 of these you’re off to a great start. Keep going. If you don’t have all the answers, that’s totally fine. We can help you think through all of the questions above. These are just some introductory questions we often cover so we can start to figure out the size of your project.
Reach out when you’re ready to figure out your app’s next steps!